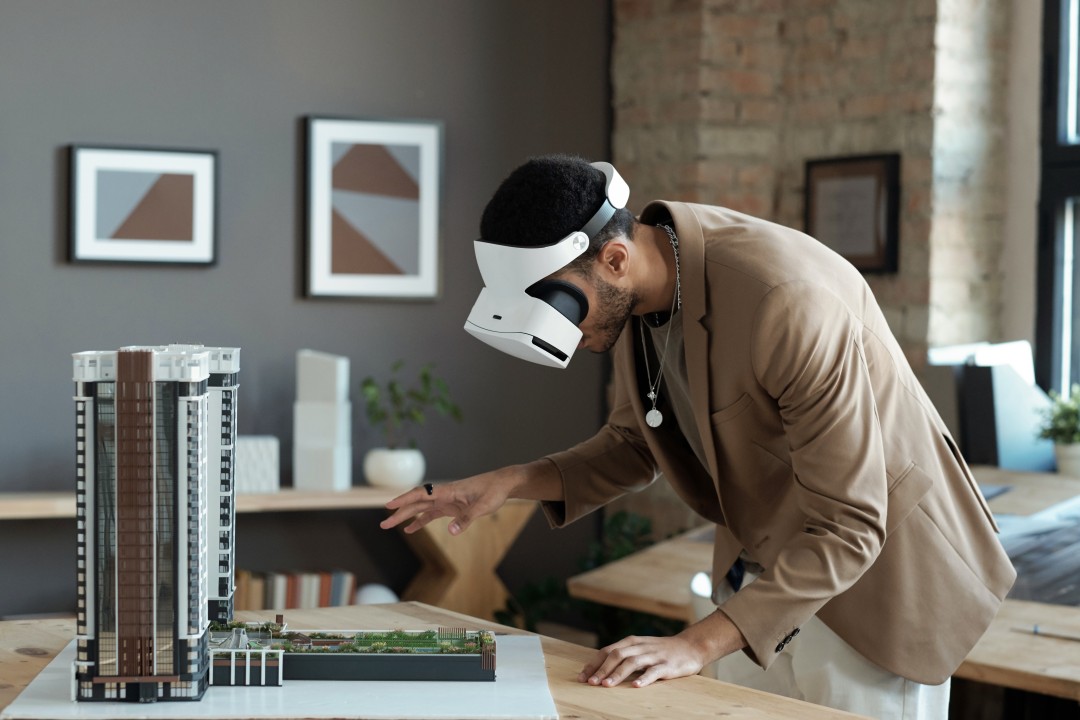
Augmented Reality (AR) is one of the most exciting and rapidly evolving technologies of the 21st century. It merges digital content with the physical world, allowing users to interact with virtual objects in real-time, in the environment around them. From gaming and entertainment to education and healthcare, AR is transforming industries and offering new ways for people to engage with information and experiences.
What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented Reality (AR) overlays digital content—such as images, sounds, and other sensory enhancements—onto the real world. Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which immerses users in a completely digital environment, AR enhances the physical world by adding layers of interactive content. This is typically achieved through devices like smartphones, tablets, AR glasses, or headsets.
The Impact of Augmented Reality
- Enhanced User Experience: AR offers an immersive and interactive experience that enhances how users interact with products, services, and content. Whether it’s trying out furniture in your home before buying it or getting step-by-step navigation in real time, AR makes experiences more engaging and personalized.
- Revolutionizing Education and Training: In education, AR provides an interactive way to learn complex subjects. Students can explore 3D models of the human body, historical artifacts, or even outer space, making learning more engaging and effective. In professional training, AR allows for realistic simulations, such as practicing surgery or repairing machinery, without the risks associated with real-world practice.
- Transforming Retail and E-Commerce: AR is reshaping the retail industry by allowing customers to visualize products in their own space before purchasing. For example, AR apps enable users to see how clothes will fit, how makeup will look, or how furniture will appear in their home, reducing the uncertainty that often comes with online shopping.
- Advancing Healthcare: In healthcare, AR is being used for everything from enhancing the visualization of complex surgeries to providing real-time information during medical procedures. AR can also be used in patient education, helping individuals better understand their conditions and treatment options through interactive models and simulations.
- Innovating Entertainment and Gaming: Perhaps the most well-known application of AR is in gaming and entertainment. Games like Pokémon GO have popularized AR by blending the virtual and physical worlds, creating a new type of gaming experience that encourages players to explore their real-world environment.
How Does Augmented Reality Work?
AR technology works by combining data from the real world with digital information to create an interactive experience. This process typically involves the following components:
- Sensors and Cameras: AR devices use sensors and cameras to gather data about the physical environment. This includes depth sensors, accelerometers, gyroscopes, and GPS to detect the user’s location, movement, and orientation.
- Projection: The AR device then projects digital content onto the user’s view of the real world. This content is often displayed through a screen, such as a smartphone or AR glasses, where it is overlaid onto the physical environment.
- Processing: The AR system processes the data collected by the sensors to understand the environment and position the digital content accurately. This involves complex algorithms that recognize objects, surfaces, and patterns in the real world.
- Interaction: Finally, AR allows users to interact with the digital content as if it were part of the real world. This can involve touching, dragging, or manipulating virtual objects through touchscreens, gestures, or voice commands.
Challenges and Future of Augmented Reality
- Technical Limitations: Despite its potential, AR still faces technical challenges, such as ensuring that digital content seamlessly integrates with the real world, maintaining accurate tracking, and reducing latency. Battery life and device overheating are also common issues that need to be addressed.
- Privacy and Security: AR devices, particularly those with cameras and sensors, raise concerns about privacy and data security. Protecting user data and ensuring that AR applications are used responsibly is crucial as the technology becomes more widespread.
- Accessibility: While AR is becoming more popular, it is still not accessible to everyone due to the cost of AR devices and the technical knowledge required to use them. Making AR more affordable and user-friendly is essential for its broader adoption.
- Future Innovations: The future of AR is promising, with ongoing advancements in hardware, software, and artificial intelligence (AI). Innovations like 5G connectivity, more powerful processors, and improved AR glasses will likely make AR more immersive, reliable, and widely available.
Conclusion
Augmented Reality is at the forefront of technological innovation, offering new ways to interact with the world around us. By bridging the gap between the digital and physical worlds, AR has the potential to transform industries, enhance learning, and create immersive experiences that were once the stuff of science fiction. As AR technology continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly play an increasingly significant role in our daily lives, shaping the future of how we work, learn, shop, and play.